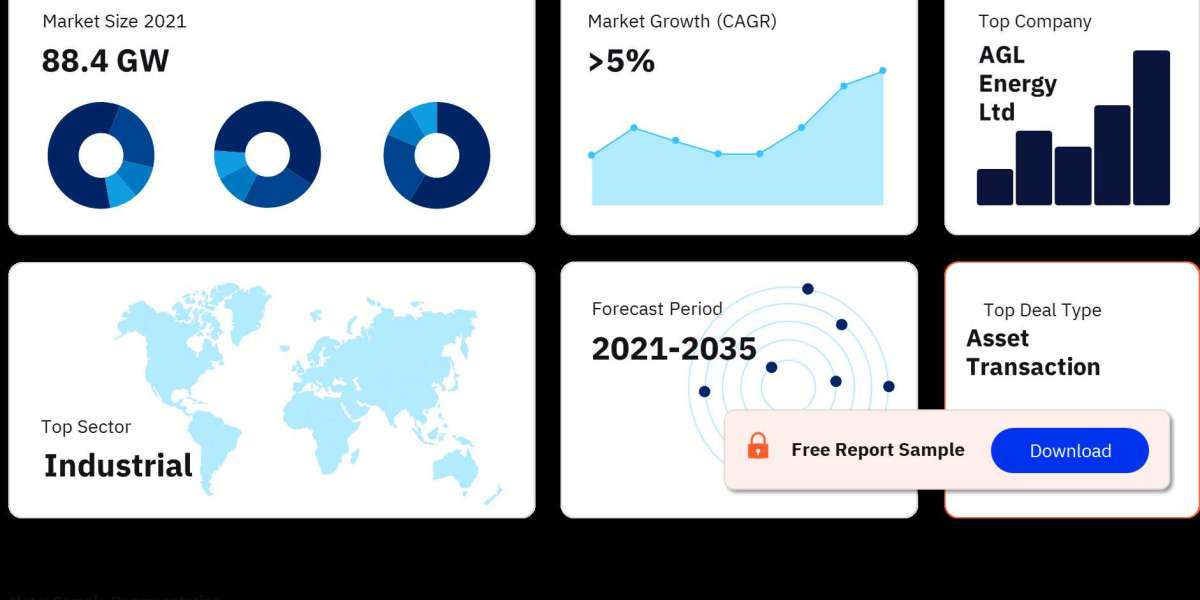
Encompassing Queensland, New South Wales, the Australian Capital Territory, Victoria, Tasmania, and South Australia, the NEM covers roughly 40,000 kilometers of transmission lines and cables. This interconnected grid caters to around 9 million customers, representing roughly 80% of Australia's total electricity consumption. Western Australia and the Northern Territory have separate electricity markets due to their geographical isolation.
Market Mechanism: Balancing Supply and Demand
The NEM operates as a wholesale market, acting as a platform for generators and retailers to trade electricity. Power stations bid their generation capacity and price into the market, while retailers forecast their customers' demand and submit bids to purchase electricity. A complex algorithm continuously matches supply and demand in real-time, ensuring a stable and reliable flow of electricity across the grid.
Key Players in the NEM
The NEM is a multifaceted system with various stakeholders:
- Generators: Companies that own and operate power stations, including coal, gas, solar, wind, hydro, and biomass facilities.
- Retailers: Businesses that purchase electricity from the NEM and sell it to consumers. They manage customer accounts, billing, and provide additional services.
- Market Operator: The Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) is responsible for overseeing the NEM's smooth operation. AEMO ensures sufficient supply meets demand, manages system security, and facilitates market competition.
The Rise of Renewables
Australia's electricity generation mix is witnessing a significant shift towards renewable sources. While coal still holds a dominant position, its share is Australia Power Market steadily declining. Conversely, solar and wind power are experiencing substantial growth, driven by factors like:
- Government Incentives: Policy initiatives and renewable energy targets by the government are encouraging investment in solar and wind farms.
- Falling Costs: Technological advancements have significantly reduced the cost of installing and operating renewable energy facilities.
- Environmental Concerns: Growing public awareness about climate change is pushing for a transition towards cleaner energy sources.
The NEM plays a crucial role in facilitating this transition. By enabling the integration of renewable energy into the grid and providing fair competition between various sources, the NEM is paving the way for a more sustainable electricity future for Australia.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Despite the progress, the NEM faces challenges in its path towards a renewable-powered future:
- Intermittency: Solar and wind power are inherently variable, depending on sunlight and wind availability. This intermittency can create grid stability issues.
- Transmission Infrastructure: As renewable energy sources are often located far from population centers, significant upgrades to the transmission network are necessary to ensure efficient power transmission.
- Storage Solutions: Large-scale energy storage solutions are needed to balance the variable nature of renewables and ensure a reliable electricity supply.
Addressing these challenges will require ongoing investment in grid modernization, storage technologies, and advancements in renewable energy integration.
Buy Full Report For More Information on The Australia Power Market Forecast, Download a Free Report Sample